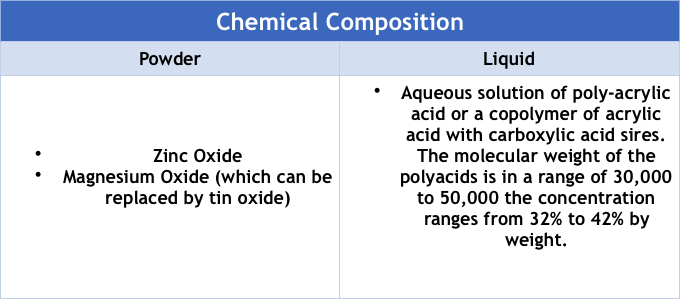
Polycarboxylate cement (also called zinc polyacrylate cement), is the first cementing system that arose as a result of the effort to obtain an adhesive cemented agent that could be firmly attached to the tooth structure. During this post we will analyze its chemical composition, as well as its characteristics and use.
Unlike zinc oxide, zinc polycarboxylate presents a strong force/strength to traction and compression. Its liquid component is polyacrylic acid, which owing to its high molecular weight prevents pulp sensibility since their molecules are large and can not traverse the peritubular space acting as sealants.
Adhesion to the dental structure
- Presents chemical adhesion to the dental structure.
- It is believed that it reacts with calcium ions on the surface of the enamel or dentine by the carboxyl groups, so the adhesion strength is greater in the enamel than in the dentine.
Work time and setting
- Work time is much much shorter (approximately 2.5minutes).
- Working time and setting Reduced the temperature of the reaction can increase the working time. The disadvantage is that the cold tile can cause the polyacrylic acid to thicken, which makes mixing difficult.
- The only thing recommended is to refrigerate powder.
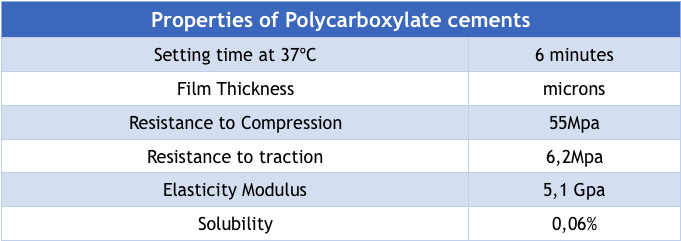
- Setting time in between 6 and 9 minutes.
Mechanical properties
- The compressive strength oscillates approximately between 55 and 67 MPa, lower than zinc phosphate.
- Not as rigid (2.4 a 4.4 MPa) as the Zinc Phosphate.
- It is not as fragile as zinc phosphate.
- Due to its potential for plastic deformation, it is much more difficult to remove excess cement.
Solubility
- Its solubility is low in water, but it increases when exposed to organic acids with a PH of less than 4.5.
- As the reduction P / L produces a greater solubility.
Biological Considerations
- The pH of the liquid is 1.7, which is neutralized by the powder.
- Therefore, the PH of the mixture increases rapidly as the setting reaction occurs.
Manipulation
- The liquid is very viscous, which is a function of the molecular weight and the concentration of polyacrylic acid, parameters that vary from one brand to another.
- This cement must be mixed on a surface that does not absorb liquid (example: glass tile).
- The liquid should not be dispensed before the mixture is to be made, since it can lose water by evaporation which produces an increase in viscosity.
- The powder is incorporated in large quantities.
- If you want to get a proper adhesion with the tooth surface, the cement should be placed on the teeth before they lose their bright appearance.
Mixing Polycarboxylate for Permanent Cementation
Surface preparation and retention
- The cement does not bond with noble metals when the model or vacuum is contaminated.
- It is essential to clean the contaminated surface of the prosthesis cavity so that it improves the wettability and mechanical adhesion at the dental cement interface.
- This surface can be eroded carefully with a small stone or by abrasive blasting with high-pressure alumina.
- After this exposure of the metal, the casting must be rinsed to remove the residues and then dried.
- A thorough cleaning of the surface of the cavity must be carried out to ensure intimate contact and favor the interaction between tooth and cement.
- The cavity must be isolated to avoid contamination.
- Absorption with cotton before cementing is considered adequate drying.
Removal of excess cement
- Excess cement must be removed when the cement has hardened completely.
- Another possibility is to start removing the excess cement as soon as it has finished setting.
- The objective of these two methods is to avoid the removal of excess cement in the plastic phase.
It has an acid-base reaction when its components are mixed. Adhesion to the tooth is chemical, and this happens when the free radicals of the carboxyl acid group bind to the calcium of the tooth. Its components are mixed in proportion of 2.5 grams of powder and 0.10 mg of liquid. After placing the cement in the work space, the excesses should be eliminated before its setting, since once hardened it is difficult to remove.
They are not ideal for cementing because they do not support occlusal stress because of its low resistance to compression. Also, just like Zinc Phosphate cement they usually report poor marginal sealing related to the thickness of the film, which when exceeding 25 microns suffers from the adaptation of its environment.
At Dentaltix, we recommend you the following product:
Ultradent- Ultratemp regular Kit provisional cemen of polycarboxylate de Ultradent.
If you enjoyed this post or found it useful, keep an eye out for the next ones about Dental Glass Ionomer and resin cements ;)






