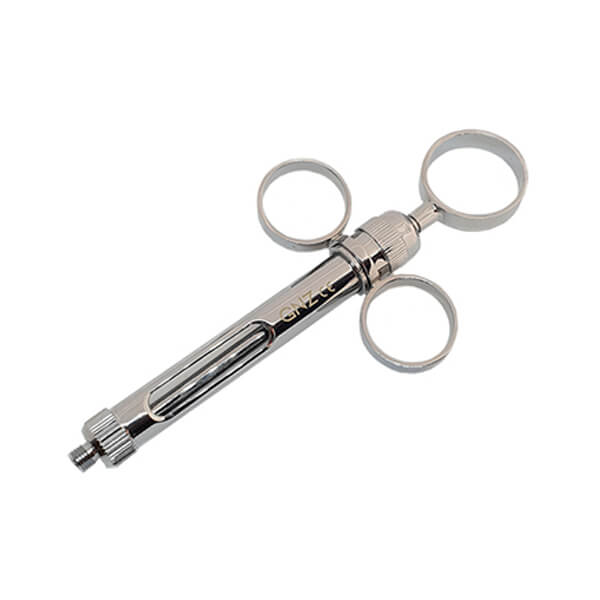
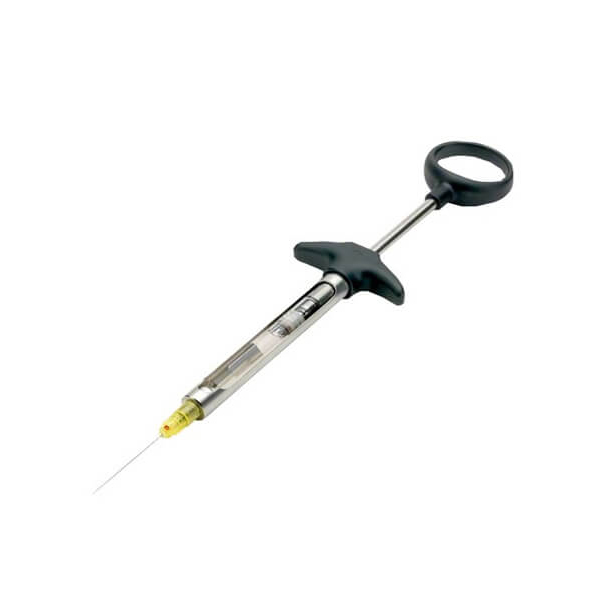
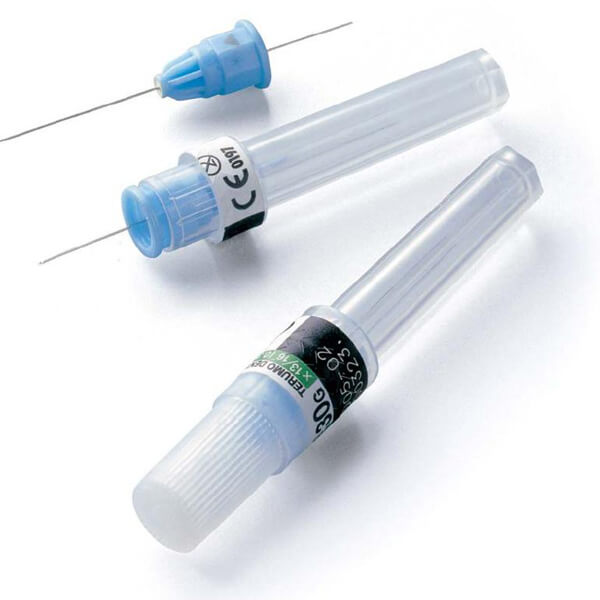
The anesthesia is an essential technique used daily in all dental clinics. The anesthesia needles and syringes, are one of the most used dental instruments in dentistry. Why? Because they prevent the patient from feeling discomfort during dental treatment and allow procedures to be carried out that would be impossible without them.
Anesthesia aims to eliminate the sensitivity of a specific area, in this case, the mouth. It numbs the tooth and gums so that dental treatment can be carried out painlessly and comfortably. For this purpose, anesthesia can be applied with different types of instruments and in different ways.
Due to the great importance of these instruments and the need to know them in depth, today we bring you a post where we tell you everything you need to know about anesthesia needles and syringes and help you choose the ones that best suit each clinical situation! Stay tuned because... we're getting started!
The most commonly used anesthesia in the dental sector:
Today there are different types of anesthesia. Opting for one method or another depends on the type of dental treatment required by each patient. In dentistry, local anesthesia is the most commonly used technique to eliminate oral sensitivity since it can be applied in any treatment of the mouth that generates discomfort or pain. It is ideal for interventions such as: endodontics, fillings, extractions or implants. But this is not all, although it is not usual, the professional can also use local anesthesia for a treatment of dental hygiene with a lot of subgingival dental tartar and plaque.
We distinguish between 2 types of local anesthesia:
- With vasoconstrictor: vasoconstrictor is added to the local anesthetic in order to provide deeper anesthesia and hemostasis in the treatment area, which is especially useful for many dental procedures. In addition, the vasoconstrictor helps to prevent toxic reactions of anesthetic drugs, decrease their plasma concentration and prolong their action. The most common vasoconstrictors used are adrenaline and felipressin. Caution should be exercised with their use in hypertensive patients, patients with coronary artery disease, hyperthyroid patients and, due to their metabolic effects, in diabetic patients.
- Without vasoconstrictor: it is used in short treatments or in patients in whom vasoconstrictor cannot be applied due to its possible adverse effects.
Types of anesthesia in the dental clinic:
The types of dental anesthesia are classified as follows:
- Topical anesthesia: is applied in the form of a gel or spray. It is characterized as a comfortable and less bothersome method. However, the duration of effect is shorter and is only superficial.
- Infiltrative anesthesia: is the most commonly used anesthetic technique in dentistry, also called periapical or supraperiosteal. It is based on the injection between the mucosa and the periosteum at the apex level so that the anesthesia reaches around the nerve endings through the periosteum and the outer cortex of the bone.
- Trocular anesthesia: consists of the infiltration of a local anesthetic in the proximity of a nerve trunk to anesthetize its entire territory. It is also called locoregional or nerve block. There are several techniques for the upper and lower jaw, some of them are the Spix or intrabuccal technique, the cutaneous or extrabuccal technique, the gow-Gates technique, the Carrea technique, etc.
- Intrapulpal anesthesia: is a technique used in cases of acute pulpitis when anesthesia is not achieved with other techniques and consists of injecting anesthesia into the pulp space. Its application is painful, it is recommended to explain to the patient.
- Intraligamentary anesthesia: is an anesthetic technique that is applied with a very fine needle and is useful for all types of minor interventions on single teeth. It is also used as a complementary technique when complete anesthesia is not achieved with another technique.
- Intrapapillary anesthesia: It is used as a complementary technique to obtain deeper anesthesia or due to the existence of accessory innervation.
Anesthesia techniques:
Once you are clear on the type of anesthesia best suited to the relevant treatment, it is time to consider a number of issues:
- Disinfection.
- Selection of the needle.
- Mucosal barrier penetration.
- Suction.
- Needle insertion.
- Injection of the anesthetic.
- Volume of the anesthetic solution.
- Anesthetic temperature.
- Injection speed.
- Waiting time.
- Subsequent recommendations.
How to choose a syringe for dental anesthesia?
The use of syringes to administer anesthesia is fundamental in dentistry. The anesthesia syringes are the vehicle that transports the anesthetic tube and the needle to perform the anesthetic infiltration. Currently, the most commonly used in dental clinics are the reusable metal ones. These are made up of 4 parts:
- Body: this is the hollow, cylindrical shape inside which the anesthetic tube is placed.
- Coiled tip: it is located on the inside and the needle is inserted into it. This allows it to be attached to the end of the syringe body securely and firmly.
- Piston or plunger: it has a special design that allows it to attach to the rubber cap of the tube.
- Clamping area: located at the other end of the syringe. It can be T-shaped or ring-shaped. In this zone the fingers are supported and the piston is pushed.
Types of dental anesthesia syringes
Cartridge back-loading metal aspirating syringes:
 They are the most commonly used in dentistry. Their advantages are that their cartridge is visible, aspiration can be performed with one hand. In addition, they are autoclavable and corrosion resistant. However, they are heavier than others and their size is too large for certain people.
They are the most commonly used in dentistry. Their advantages are that their cartridge is visible, aspiration can be performed with one hand. In addition, they are autoclavable and corrosion resistant. However, they are heavier than others and their size is too large for certain people.
Go to Ultracalm Plus Anasthesia Syringe
Back-loading, cartridge-loading, plastic aspirating syringes:
They do not have a typical clinical appearance, are very light, the cartridge is visible and allow the dentist to aspirate with one hand. In addition, they are corrosion resistant, so they have a long life and are cheaper. The main disadvantage is that they can deteriorate more easily due to sterilization.
They do not have a typical clinical appearance, are very light, the cartridge is visible and allow the dentist to aspirate with one hand. In addition, they are corrosion resistant, so they have a long life and are cheaper. The main disadvantage is that they can deteriorate more easily due to sterilization.
Back-loaded metal auto aspirating syringes:
This type is intended for significant suction of more than 10-15%. As in the previous models, their cartridge is also visible, they are very easy to aspirate and can be autoclaved. In addition, their corrosion resistance is long lasting and they contain the graduated piston. The main disadvantage is their heavy weight, which makes them more "unsafe" for the dentist.
Jeringas de presión:
Pressure syringes:
This type of syringe provides good anesthesia to the gingiva, accompanied by a mechanical advantage, which gives the dental professional a very quick and easy application. The cartridges are protected by the syringe and the dentist can dose the applied dose. In addition, this type of syringe overcomes tissue resistance.
Disposable syringes:

This type of syringes are single use, very light, sterile and cheaper than the previous types. They do not accept cartridges, are more difficult to handle, aspiration is difficult and they are not indicated for dental anesthesia. In dentistry, they are widely used in endodontic irrigation. The best option for dental anesthesia are the syringes mentioned above.
Aspects to take into account regarding dental syringes
Once the types of dental syringes most commonly used in the dental sector have been clarified, it is necessary to clarify a series of aspects that it is essential to take into account in order to make the right choice:
- It is important that they are durable and capable of withstanding repeated sterilization processes without deteriorating.
- Ideally, they should be able to accept a wide range of cartridges and needles from different manufacturers and, in addition, allow for repeated use.
- Find out if they are simple to use with one hand and lightweight.
- They should provide effective suction and be designed so that the blood in the cartridge can be easily observed.
Definitely, the most recommended syringes for dental practice are the aspirating syringes because, as we have already seen, aspiration is performed with one hand thus reducing effort and improving handling. Moreover, as regards aspiration, it is recommended to perform it before injecting the anesthetic to be aspirated and to repeat it every 0.25-0.50 ml.
Which needle do I go with?
Once we've told you all you need to know about dental syringes, it's the anesthesia needles's turn. They were introduced to the market in the year 1853. Since then, they have been made strong, thin, sterile, flexible and indicated for one use only per intervention and patient. In addition, they come in sterile plastic containers and thus reduce the risk of cross-infection.
Dental needles are the instruments responsible for delivering the anesthetic from the cartridge to the tissue. Currently, the most commonly used needle materials are base metal alloys such as chromium, nickel or cobalt, which are resistant to corrosion and heat. As for the parts into which a needle is divided, the following are distinguished:
- Bisel: helps penetration by being angled and decreases color intensity. It can be long, medium or short. The most common inner diameter is usually 0.2mm and the outer diameter is 0.4mm.
- Shaft: refers to the length of the needle. It starts at the bevel and ends at the part that penetrates the cartridge.
- Connector: is where the needle fits. It can be made of metal or plastic.
- Syringe adapter: this is the end part of the connector and is threaded.
- Bore: this is the internal diameter of the needle lumen. It is important for aspiration and for the amount of anesthetic to infiltrate.
Types of dental needles
With regard to the types of anesthesia needles, different types are distinguished based on gauge and length. The gauge is expressed in mm with the letter G. They range from 25G to 30G gauges. The most common are 25G, 27G and 30G.
The smaller the gauge of the needle, the more flexion is provided and, therefore, provides muchless suction to the dentist. On the other hand, the larger the gauge, the greater the precision, thus reducing the possibility of breakage. In addition, the finer the needle, the slower the aspiration will be.
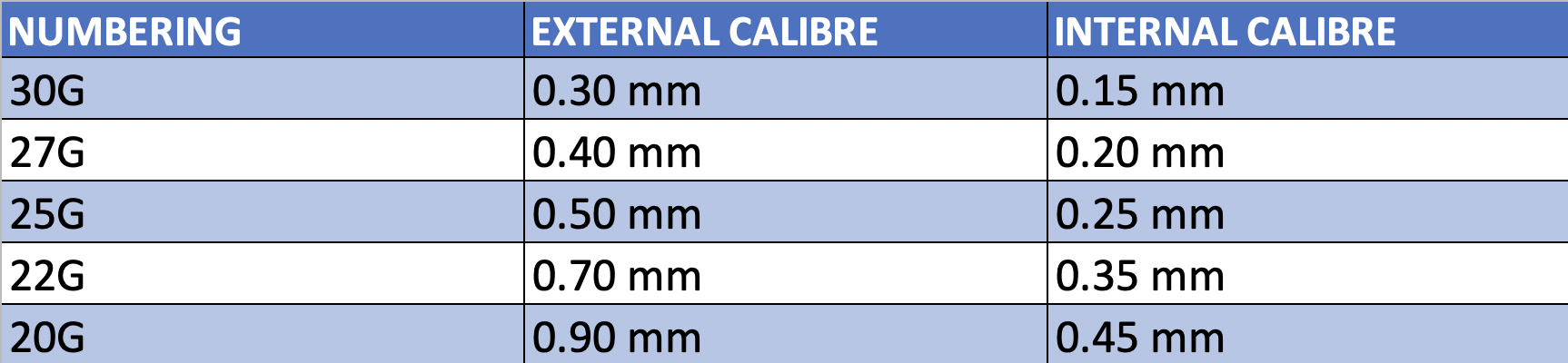
On the other hand, the needle length also serves to differentiate one from another. They can range from short (10 mm) to long (32 mm).
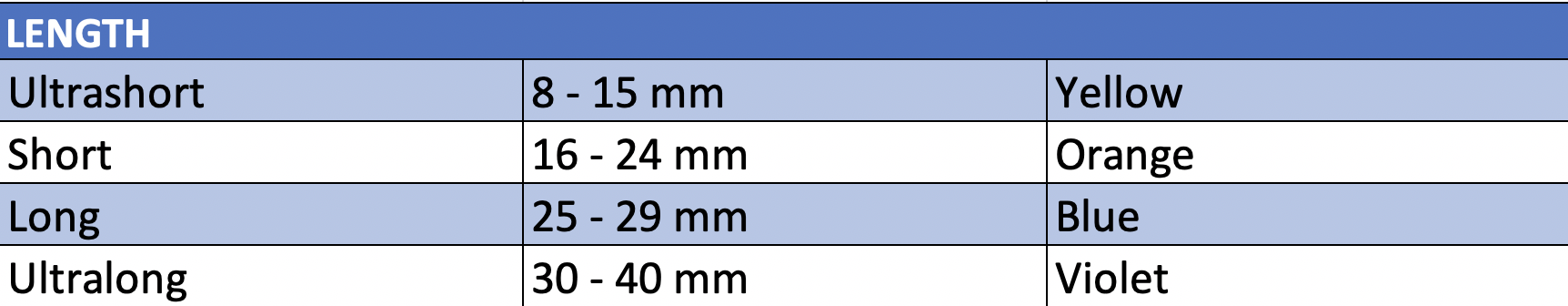
Tips for the care and handling of anesthesia needles
Now that you are clear about all the types of anesthesia needles that exist, we reveal a series of tips on their care and handling!
- The needles should not be used in more than one patient.
- They should be changed after several tissue penetrations.
- It is important that they are transported with their protective case.
- To avoid accidents, never lose sight of the needle tip.
- It is important not to force a needle against a resistance.
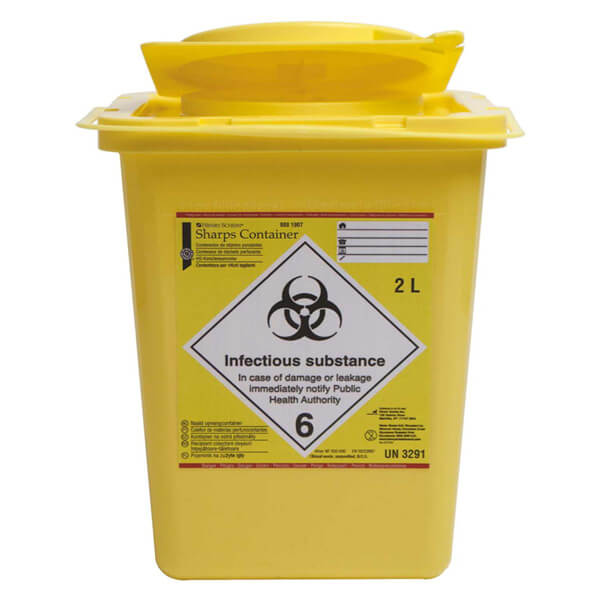
- They must be deposited in sharps containers.
- At the time of inserting the needle in the specific containers, it must be covered or, if there is more than one, it is necessary to store them in some container that allows them to be transported without risk.

Source: Henry Schein
The most common accidents with dental needles
We couldn't end this post without mentioning some of the most usual accidents that occur with dental needles:
- Needle breakage due to improper insertion and sudden movements of the patient.
- Easier plastic-needle bonding.
- Possible manufacturing defect.
- Length of the shank to identify the broken fragment.
- Inferior dental nerve anesthesia.
- Accidental puncture of the patient.
- Accidental puncture of the practitioner, when recapping the needle. This is the most frequent. It is recommended not to recap in the air.
That's it for today's post on anesthesia needles and syringes. As you have been able to see it is an arduous subject in which it is necessary to take into account many factors and, above all, the clinical situation, before choosing one or the other. We hope we have solved all your doubts and, if you have any other, do not hesitate to write to us! We will be happy to help you.
And remember it is important to keep these tips in mind because... prevention is cure!
See you next time!