Dental burs are metal instruments used by dentists for precise cutting, polishing and grinding. They are used in rotary dental instruments such as turbines, contra-angles and hand pieces. There are numerous burs specifically designed for different areas of dentistry. There are so many types, shapes, sizes and grits available, so we can assure you it's a very interesting topic. Want to know more about dental burs? Then keep on reading!
ISO classification of dental burs
In our article Guide to the different types of dental burs we told you all about dental burs, however we want to go more in depth about their classifications to make the process of finding exactly what you're looking for easier than ever before.
In this image you can see a dental bur with its ISO code.
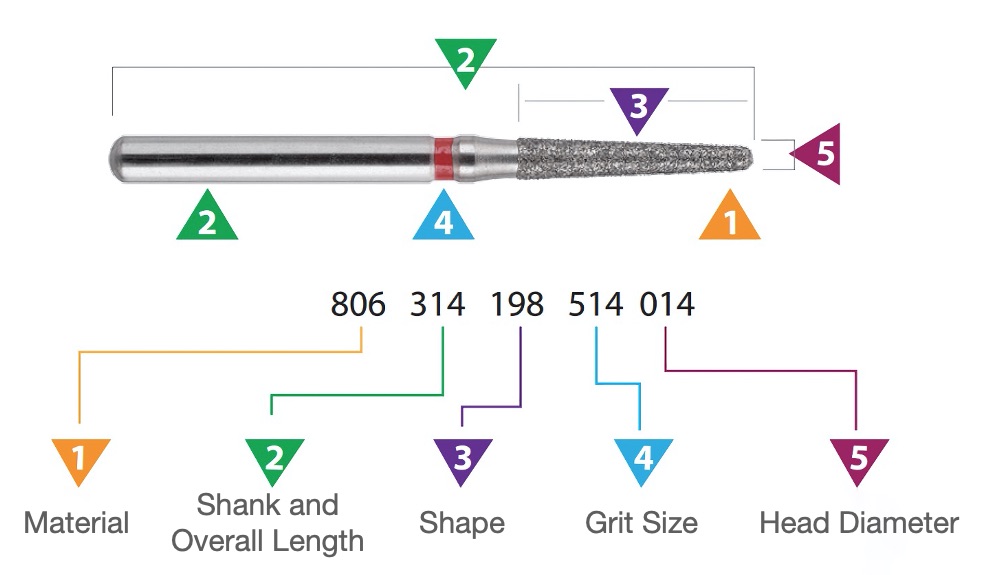
A good way to understand all about dental burs is to start by considering the 5 aspects which the ISO classification takes into account:
- By type of material
- By shank
- By shape
- By grit size
- By head diameter
1. Classifying dental burs according to the type of material
The composition of dental burs is a crucial consideration. In the past they were made of steel, but nowadays new materials have emerged that provide improved cutting qualities and durability. We can distinguish between two main types:
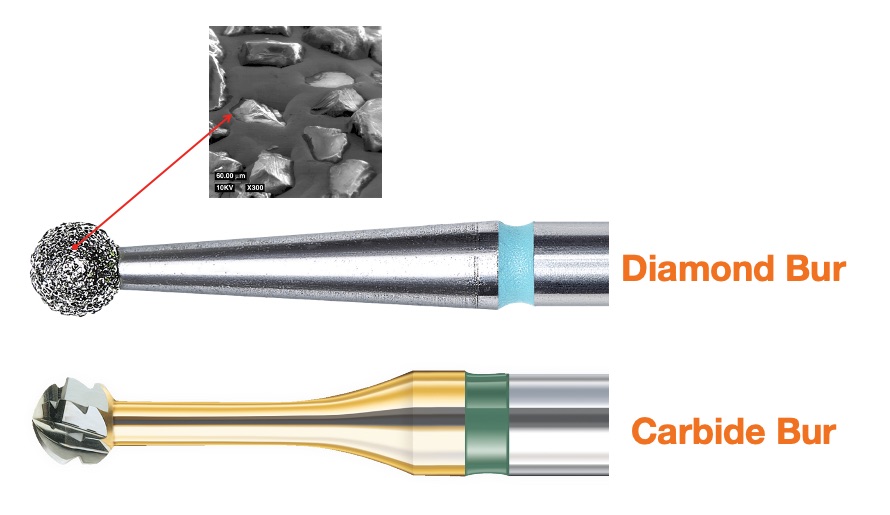
- Tungsten carbide dental burs (carbide burs): This material is becoming the replacement for the older steel burs. Tungsten carbide has three times the rigidity of steel and is highly efficient, as well as being highly durable due to its outstanding wear-resistant properties.
- Diamond dental burs: Diamond is the hardest natural material known to man and, therefore, is the material of choice when it comes to wearing down the hardest tissue in the human body: tooth enamel. Diamond burs have a steel shank and an active part coated with natural or synthetic diamond powder. The vast majority of commercially available dental burs are made of synthetic diamond and it is less common to come across natural diamond burs. Manufacturers who use natural diamond usually emphasise this characteristic, as it gives the burs greater quality, efficiency and durability. Of course, the cost of a natural diamond burr is higher than that of a synthetic diamond burr.
2. Classifying dental burs according to their shank
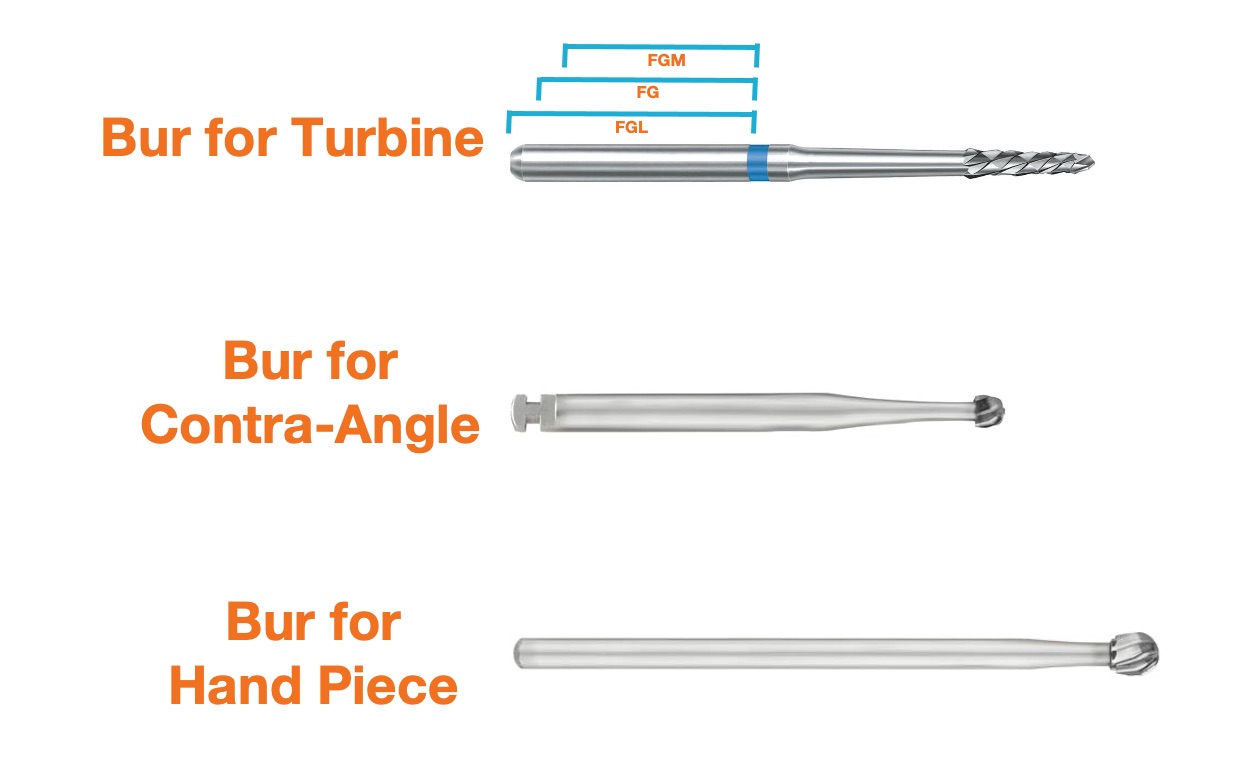
This is the second simplest classification and the differences between the three types lie in their size, the speed at which they can work and their functions. There are:
- Turbine dental burs: Undoubtedly the fastest rotary instrument calls for a dental bur with special features. The end is exposed and the diameter of the shank is 1.6 mm. They are also known as high rotation burs, high speed burs or FG burs (Friction Grip). Additionally, referred to by the acronyms FGM (Friction Grip Mini) or FGL (Friction Grip Long) according to their shank length.
- Contra-angle dental burs: Their diameter is 2.35 mm and commonly you'll see a notch at the non-active end. They are also known as RA burs (Right Angle), CA burs or simply low-speed burs.
- Hand piece burs. Like the contra-angle burs, the shank diameter is also 2.35 mm, but it is a considerably longer bur. It is also known as a HP bur or bur for straight dental hand pieces.
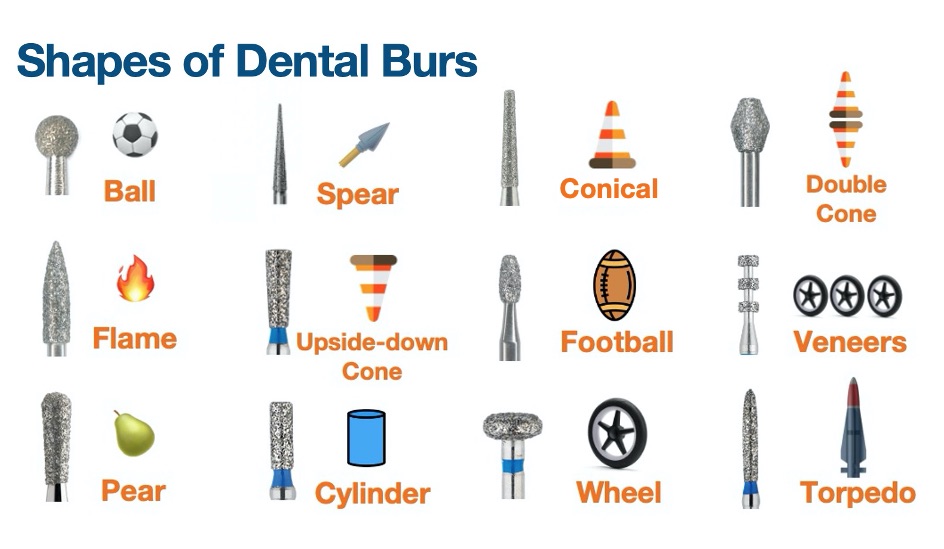
3. Classifying dental burs according to their shape
There are so many of them! They are named after their similarities to other, more everyday, objects. Here are just a few:
- Ball burs: Perhaps the most common of all, they are used to open cavities or create retentions in dental surgery and also to create grooves for prosthetics. They are also useful for opening and shaping the pulp chamber after pulpotomy.
- Cylindrical burs: There are flat-tipped, round-tipped and pointed burs, each designed for a particular purpose. For example, the flat-tipped cylindrical bur is used for shaping the chamfer in ceramic crown preparations.
- Conical burs: There are rounded and flat-tipped burs. The latter, for example, is used for inlay preparations or for chamfering and counter-chamfering the finishing line, among other uses.
- Inverted Cone burs: Among other applications, its uses include the opening of cavities or creating retentions (undercuts) in dental surgery. It can also be used to form the occlusal surface.
- Flame burs: It's the ideal shape to allow a delicate definition of the proximal or buccolingual walls in surgery or prosthetics.
- Wheel Bur: This is often used to create mechanical retentions, deep cuts and occlusal shapes.
Besides these, there are more shapes such as: torpedo bur, cylindrical bur, rugby or football bur, spear bur, double cone bur, pear or pyriform bur and many more.
This image can help you visualise them!
At Dentaltix you can find burs sorted by shape, take a look at our wide variety: View all burs
4. Classifying dental burs according to their grit size
The grit size of dental burs determines how aggressively they are able to erode the tooth. The coloured ring, which is usually found on the neck of the bur, determines the coarseness of the grain. This coding is standardised by the ISO regulatory and the most common colours are:
- White: Superfine
- Yellow: Extra fine
- Red: Fine
- Blue: Standard
- Green: Coarse
- Black: Super Coarse
5. Classification of dental burs according to head diameter
This is the most concise classification of dental burs. The size of the bur is determined by the diameter of the active part of the bur and there are many, many different sizes.
Now that we know these 5 classifications of dental burs, it should be really easy to understand ISO coding. This coding allows us to speak the same language when choosing a dental bur from various manufacturers.
What other types of dental burs are there?
The world of dental burs is very broad and it doesn't end here, there are also other types of dental burs that are designed for specific dental procedures, for example:
Dental laboratory burs: in this category there is a wide variety of dental laboratory burs designed for working on metal, plaster, ceramics, acrylics, etc. Here you can see all of our dental laboratory burs.
Dental and maxillofacial surgery burs: there is a wide variety of burs for different surgical actions, e.g. bone cutting burs, alveolar ridge expansion burs, sinus lift burs, dental implantology burs, etc.
Endodontic burs: In this category you will find everything from burs for endodontic cavity opening to burs for canal preparation, such as Peeso burs and Gates Glidden burs. Here you can see all of our endodontic burs.
Frequently asked questions and tips about dental burs
We've compiled some frequently asked questions, as we want you to know everything!
When should I buy a new burr?
We recommend changing the bur after five clinical uses. In doing so, you avoid considerable wear and, as a result, avoid damaging the pulp from the heat generated by excessive friction.
Can I use a turbine bur in a contra-angle handpiece?
Of course! But you must have this adaptor.
How should I clean my diamond burs?
We advise you to always clean your burs after each use by removing the residues with a brush or in an ultrasonic tank with an enzymatic detergent solution, the latter option is the best to maintain their abrasive power.
How can I prevent my burs from rusting?
It's very simple! Choose cleaning and disinfecting solutions with corrosion protection, always follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding concentration and application time. Here you can find the bur disinfectant you need.
We know that dental burs come in a huge variety and it can be confusing to find the right one. We'd love to hear from you if we've made your job easier, we always appreciate it if you can get in touch and share your suggestions.
Follow us on our social media channels to find out what's new and continue to brush up on your knowledge.
See you soon!





