Among dental rotary instruments, the contra-angle handpiece plays an essential role due to its precision, versatility and ergonomics. From conservative dentistry procedures to implantology and prophylaxis, this instrument allows you to work with control and comfort even in the most difficult areas of the oral cavity.
Its characteristic angled shape and its ability to transmit energy from the micromotor to the bur make the contra-angle handpiece an indispensable tool in modern clinical practice. In addition, technological advances have significantly improved its design, offering lighter, quieter and more durable models, adapted to different dental specialities.
Below, we will explore in detail what a dental contra-angle is, how it works, how it differs from a turbine, what types exist and how to choose the most suitable one for each treatment. Let's get started!
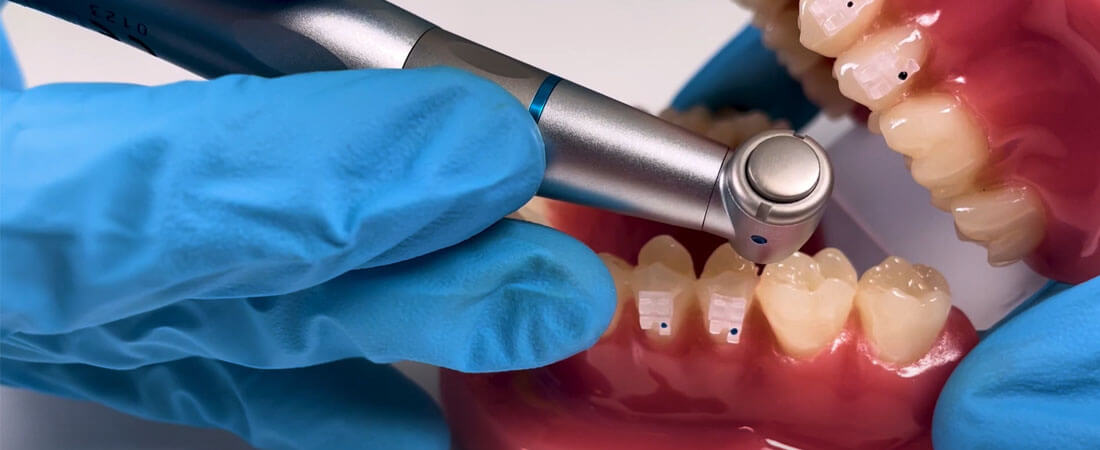
What is a dental contra-angle?
The dental contra-angle handpiece is a rotary instrument designed to transmit the movement generated by a micromotor (electric or pneumatic) to a bur or rotary accessory, allowing various clinical tasks to be performed with precision and safety. Its main feature is its angular shape, which improves visual and physical access to the posterior areas of the mouth, facilitating the dentist's work without compromising ergonomics or visibility. It consists of three main parts:
- Head: Located at the top, this is where the bur or rotary instrument is inserted. It may have different clamping systems (pressure, clip, or button) depending on the manufacturer.
- Body or Handle: This allows for a comfortable and non-slip grip, ergonomically designed to reduce fatigue for the professional during long workdays.
- Rear Connection: This is the area that connects to the micromotor. Power, speed, and, in more advanced models, the air, water, and light necessary for optimal operation are transmitted through this connection.
Contra-angle handsets are manufactured from materials such as stainless steel or titanium, which offer excellent wear resistance, are very lightweight, and can be autoclaved. This combination of design and materials makes them highly durable and reliable instruments.
How does it work and what is it used for in dentistry?
The operation of the contra-angle handpiece is based on an internal gear system that transmits the movement from the micromotor to the bur. Depending on the gear ratio, the instrument can increase, decrease, or maintain the motor speed, thus adapting to different clinical needs.
This speed and torque control allows the professional to work with precision in treatments requiring everything from high power to more delicate manipulation. Common applications include cavity and crown preparation, filling removal, dental cleaning and polishing, endodontics, oral surgery, and implant placement.
Its versatility makes the contra-angle handpiece an indispensable tool in almost every area of modern dentistry.How does it differ from using a dental turbine?
Although both belong to the rotary instruments, the contra-angle handpiece and the dental turbine present notable differences in their operation and application:
| Contra Angle | Turbine | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy source | Electric or pneumatic micromotor. | Direct compressed air. |
| Rotation speed | From 20.000 to 200.000 rpm. | Up to 400.000 rpm. |
| Torque (force) | Tall, ideal for controlled work. | Low, higher cutting speed. |
| Noise level | Low, quiet operation. | Higher, due to the airflow. |
| Clinical applications | Endodontics, implantology, restorations, prophylaxis. | Rapid grinding, removal of hard tissue, tooth reduction. |
| Control and precision | Greater control, minimal vibration. | Less control, high speed. |
Types of Dental Contra-Angle Handpieces
There are different types of contra-angle handpieces, and they can be classified according to two main criteria: the transmission ratio (that is, the speed and torque they transmit from the micromotor to the bur) and the dental specialty in which they are used. Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the most suitable model according to each professional's clinical needs.
Classification according to transmission
According to the transmission ratio, we find three main types of contra-angles: direct transmission (1:1), reduction, and multiplication.
- Direct-drive contra-angles, identified by their blue color, transmit the micromotor's speed directly, without amplifying or reducing it. They are ideal for treatments requiring constant speed and precise control, such as caries removal, restoration finishing, or some endodontic procedures. Their stable operation and low vibration offer the practitioner excellent tactile sensitivity and highly controlled handling.
- Reduction contra-angles, recognizable by their green color, incorporate an internal gear system that reduces the rotational speed but increases torque. This type of instrument is especially useful in surgical and implant procedures where strength and stability are needed more than speed. Thanks to this reduction, the risk of overheating is minimized, and precision during work is increased.
- Multiplier contra-angles, marked in red, are characterized by increasing the rotation speed, typically by a 1:5 ratio. This makes them ideal for restorative and prosthetic treatments requiring rapid material removal or the preparation of tooth structures. Their superior power allows for highly efficient work and a smooth, clean finish in less time.
Classification according to dental specialty
In addition to the transmission, contra-angles differ according to the dental specialty for which they are designed, as each area requires specific characteristics in terms of speed, torque, and ergonomics.
- Standard contra-angles are the most versatile and are used daily in most restorative and endodontic procedures. Their balanced design and compatibility with a wide range of burs make them an indispensable option for any clinic.
- In dental prophylaxis, special contra-angles are used that allow the attachment of polishing cups or brushes. These models are designed to be lightweight, quiet, and comfortable, facilitating professional cleaning without causing operator fatigue.
- Implant contra-angles feature a reinforced structure and a transmission system that offers high torque and low speed, ideal for dental implant placement. Their design guarantees maximum stability and control during the surgical phase, preventing bone overheating.
- In orthodontics, stripping contra-angles stand out, specially designed to perform controlled and safe interproximal enamel reduction. Their precision allows for creating the necessary space between teeth without damaging adjacent surfaces.
- In prosthetic and aesthetic dentistry, speed multipliers are widely used because their ability to increase speed facilitates the rapid preparation of structures and the final finishing of preparations with a high-quality surface.
Check out our best-selling contra-angles:
The dental contra-angle is an essential instrument in dental practice due to its precision, versatility, and ergonomics. Its design allows easy access to all areas of the oral cavity and optimal control in a wide variety of treatments, from restorations to surgical or prophylactic procedures.
Understanding the differences between the various types, whether in terms of their transmission system or the specialty for which they are designed, is essential for choosing the most suitable model for each clinical need. A correct selection translates into greater efficiency, comfort for the professional, and better results for the patient.
That's all for today's article! We hope you found it helpful, and if you liked it, please feel free to share it. Follow us on our social media channels to stay up-to-date on all the latest news in the dental sector and our special offers. See you soon!


